What I knew Before
Learning Theories became known to me at
university level. The first of them being Cognitive, which was developed
by a famous psychologist named Jean Piaget. I got to understand that from
this theory, children move through four (4) different stages of
mental development. These include:
1)
Sensorimotor – this stage begins from ages 0 – 2 years. Children in
this stage utilizes the skills and abilities they were born with such as
sucking, grasping and listening to learn about the environment around them.
2)
Preoperational – this stage begins from ages 2 – 7 years. Children in this
stage are more engaged in role play and using objects that is not for their
uses such as a broom for a horse. Piaget classifies this as egocentrism.
3)
Concrete Operational – this stage ranges from ages 7 – 11 years.
Children in this stage begin to understand objects and events mentally, but may
not grasp the main concept. An example of this displaying the same amount of
water in a jar but one is thin and the other is wide. It is obvious the child
will select the wide jar as having the most amount of water.
4)
Formal Operational – this stage ranges from ages 11 years – adulthood.
Children in this stage as they develop are often able to quickly plan and
organize approaches to solving a problem.
Cognitive information processing (CIP) theory is often referred
to as simply "information processing." Information processing is not
really the name of a single theory; it is a generic name applied to various
theoretical perspectives dealing with the sequence and execution of
cognitive events. Schunk (1996) offers the following helpful
summary/definition:
Information processing theories focus on how people:
- attend to environmental events,
- encode information to be learned and relate it to knowledge in memory,
- store new knowledge in memory, and
- retrieve it as needed.
Thus, learners are viewed as active seekers and processors of
information.
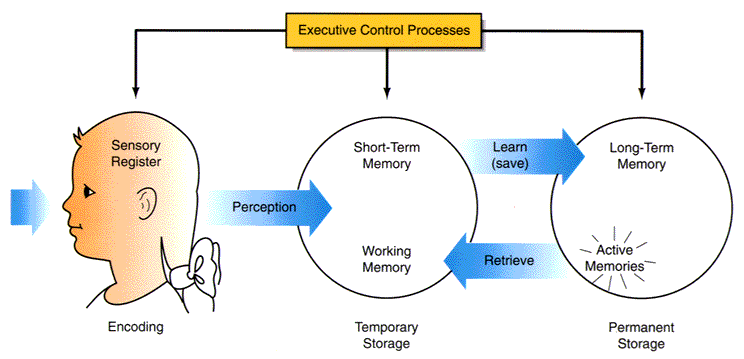
Brief descriptions of the three stages of memory follow:
- Sensory memory holds information associated with the senses (e.g., vision, hearing) just long enough for the information to be processed further (mere seconds).
- STM functions as a temporary working memory, whereby further processing is carried out to make information ready for long-term storage or for a response. Working memory holds information for a limited amount of time and holds a limited amount of information.
- LTM represents our permanent storehouse of information, capable of retaining an unlimited amount and variety of information.
Later, I learned about behaviorism through another psychologist
named B.F. Skinner. Behaviorism is primarily concerned with observable
behavior, as opposed to internal events like thinking and emotion. Observable
(i.e. external) behavior can be objectively and scientifically measured.
Internal events, such as thinking should be explained through behavioral terms
(or eliminated altogether). According to McLeod (2007), Skinner believed that
we do have such a thing as a mind, but that it is simply more productive to
study observable behaviour rather than internal mental events. He also believed
that the best way to understand behaviour is to look at the causes of an action
and its consequences. He called this approach operant conditioning.
Operant Conditioning – Skinner in his book entitled “The Behavior of Organisms: An
Experimental Analysis” defined the this term as means roughly changing of behavior
by the use of reinforcement which is given after the desired response. Skinner
identified three (3) types of responses or operant that can follow behavior.
- Neutral Operants: responses from the environment that neither increase nor decrease the probability of a behavior being repeated.
- Reinforcers: Responses from the environment that increase the probability of a behavior being repeated. Reinforcers can be either positive or negative.
- Punishers: Responses from the environment that decrease the likelihood of a behavior being repeated. Punishment weakens behavior.
From this theory, I got to understand that through
reinforcement a behavior can be determined either by a positive outcome or
a negative outcome. These may include: giving a child complement or a treat for
a job well done or spanking a child. Within this theory, there are also three
(3) principles found for teaching new and complex behaviors are defined by
behaviorists: shaping, chaining, and fading.
- Shaping
Shaping refers "the reinforcement of successive approximations to a goal behavior" (Driscoll, 2000). This process requires the learner to perform successive approximations of the target behavior by changing the criterion behavior for reinforcement to become more and more like the final performance. In other words, the desired behavior is reinforced each time only approximates the target behavior. - Chaining
Skinner also provided the explanation of the mechanism underlying the nature of complex learning. He proposed that the acquisition of complex behaviors is the result of the process referred to as chaining. Chaining establishes "complex behaviors made up of discrete, simpler behaviors already known to the learner" (Driscoll, 2000). - Fading
According to behaviorists, behaviors are acquired and exhibited because they are reinforced; non-reinforced behaviors tend not to occur. Individuals are clearly able to distinguish between settings in which certain behaviors will or will not be reinforced. The concept of fading refers to "the fading out of discriminative stimulus used to initially established a desired behavior" (Driscoll, 2000). The desired behavior continues to be reinforced as the discriminative cues are gradually withdrawn.
I could have tell that learning in
depth of these theories would have me thinking if I really want to
get in the teaching field, and yes it did, but honestly I am up for the
challenge. I may not be perfect but I can be creative.
What I know Now
Today, I am still gaining knowledge about
learning theories. Currently I am engaged in an assignment on a famous
theorist and I have chosen B.F. Skinner, simply because his
theory topped my important list when comes to teaching strategies. I
got to learn about bloom's taxonomy under cognitive, which helps in
planning lessons.
Behaviorism and cognitive theories have are both
a good way of teaching and learning processes, however, there are some
differences between them which is very significant especially for the teaching
field. While behaviorism theory’s perspective may be defined as a change of
behavior as a result of experience that can be measured, cognitive theory’s
perspective is a change in mental representation and associations brought about
by experience.
During my studies, I cannot remember going in depth on the
constructivism theory, but I have heard of it. However, through research, this
theory was developed by Jerome Bruner and it focuses on how well pupils adhere
to instructions through cognition. In the classroom, the constructivist view of
learning can point towards a number of different teaching practices. In the
most general sense, it usually means encouraging students to use active
techniques (experiments, real-world problem solving) to create more knowledge
and then to reflect on and talk about what they are doing and how their
understanding is changing.
The teacher makes sure she understands the students'
preexisting conceptions, and guides the activity to address them and then build
on them. It also focuses on how instructions are to be given to pupils. We
were encouraged to in utilizing this method, that the best way for us to really
understand what constructivism is and what it means in your classroom is by
seeing examples of it at work, speaking with others about it, and trying it
yourself. As you progress through each segment of this workshop, keep in mind
questions or ideas to share with your colleagues. I do hope that I get a
chance to study further on this theory.
How it will Affect my Teaching
Learning Theories will affect my future teaching
over one hundred percent (100%). And I state this confidently because I have
put some of them into practice through Teaching Practicum. There are two (2)
theories that stood out for me. The first is the behaviorism theory by B.F.
Skinner. By using this theory it will enable me to obtain a proper management
in my future classroom.
One example in which the behaviorism theory can
be applied in the classroom is by creating classroom rules and enforcing them
every week. In this way you can control operational conditioning where you will
obtain a positive or negative outcome. One example in which the cognitive
theory can be applied in the classroom is by questioning the pupils. Doing this
will enable thinking and with thinking comes learning. One example in which the
constructivism theory can be applied in the classroom is by grouping pupils in
a classroom to discover or experiment and come up with answers to any specific
task. In this way each pupil will develop some sort of confidence in
participation.
Behavior in pupils is an important factor in
teaching and if not controlled, teaching them does not make sense at all. The
second being bloom's taxonomy. Using this helped me with my lesson
planning preparation and I was able to
supply efficient and balanced learning objectives to the pupils.
I know when I become an enrolled teacher; these theories will be the foundation
to make my teaching grow. Not only mine, but it should be for yours
as well. I praise these theorists for their ability of helping teachers
while we help pupils.
Resources
Drisoll, M. P.( 2000). Psychology of learning for instruction.
2nd. Needham Heights, MA: Allyn and
Bacon.
McLeod, S. (2007). Skinner: “Operant Conditioning”. Retrieved on
January 20th 2015 from:
http://www.simplypsychology.org/operant-conditioning.html
Yashpalsinh, G. (2013). Comparison between Behaviourist Theory and
Cognitivist Theory.
Retrieved on February 8th 2015 from: http://www.slideshare.net/yashpalsinhgohil
1111/paper-12-comparison-between-behaviorist-theory-and-cognitivist-theory

No comments:
Post a Comment